Active Surveillance
For very small stomach GIST (size < 2cm) without high-risk features, active surveillance may be recommended. This approach involves regular monitoring using imaging studies such as CT scans or endoscopy to check for any changes in the size of the tumour.
Surgical Resection
Surgery is the primary treatment for localized gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GISTs), with the goal of complete tumour removal and recurrence prevention. A wide local resection with clear margins while preserving function is advised. Extended lymphadenectomy is typically unnecessary. Small tumours may be removed laparoscopically. However, in patients with large tumours, laparoscopic/robotic approach is discouraged because of the risk of tumour rupture. If adjacent organs are involved, en bloc resection is recommended.
If complete removal of the tumour is not feasible, physicians may administer targeted therapy prior to surgery. This approach is particularly advantageous when the tumour exhibits specific mutations that are responsive to such treatment. Pre-treatment with imatinib serves to reduce the size of the tumour, thereby enhancing surgical safety and minimizing the risk of complications such as rupture or bleeding. Typically, this therapy is administered over a period of 6-12 months before the surgical procedure. Beyond 12 months, further tumour shrinkage is uncommon, and there is a potential for the development of resistance to the treatment.
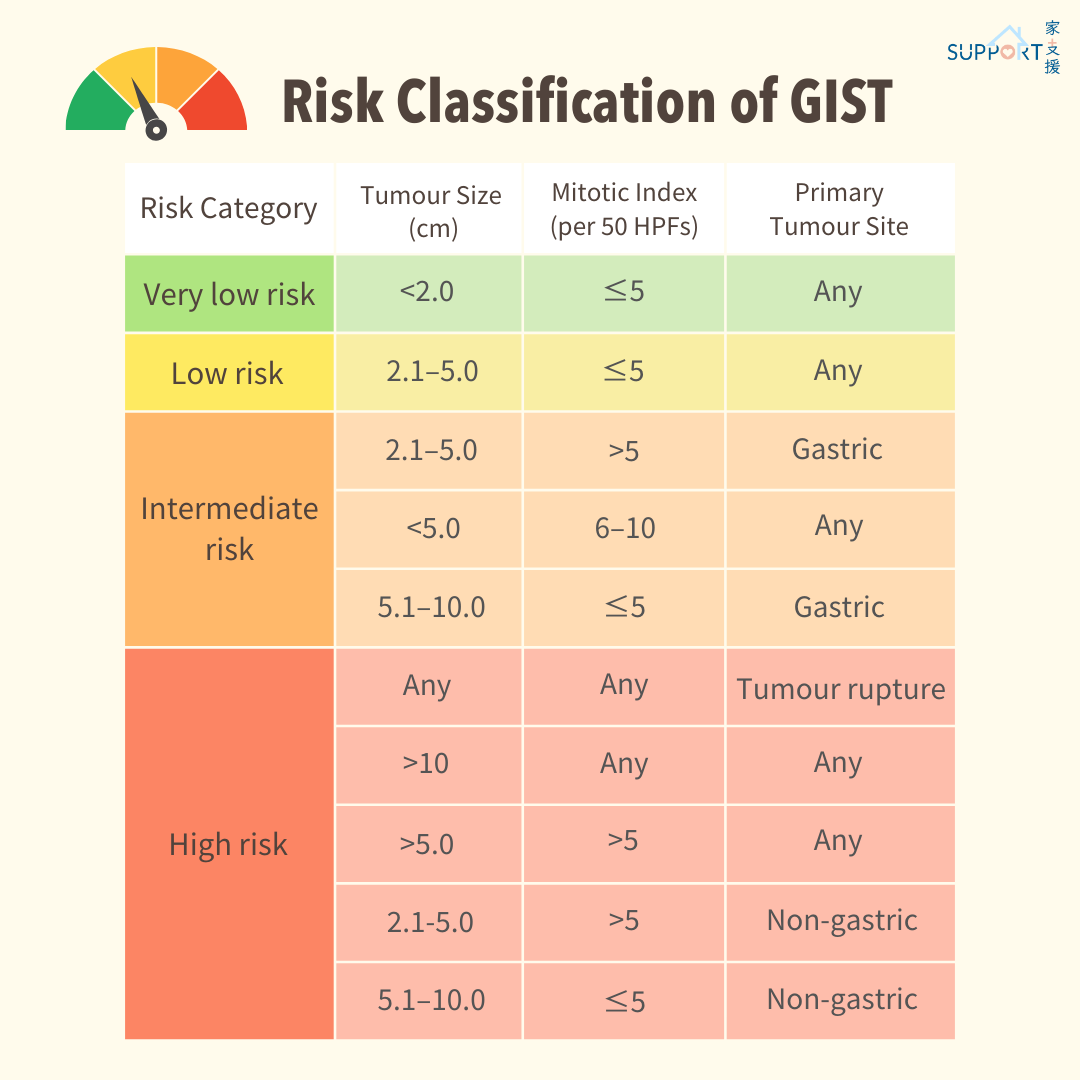
Risk Classification of GIST
Adjuvant Therapies
The doctor will determine whether adjuvant treatment is necessary based on the risk of recurrence.
| Risk of Recurrence |
Treatment Recommendations (in patient with imatinib sensitive mutation) |
| High Risk (> 50%) |
3 years of adjuvant imatinib |
| Intermediate Risk (10-50%) |
Consider adjuvant imatinib after discussing the risks and benefits with the patient |
| Low Risk (<10%) |
Should not be considered for adjuvant imatinib |
Adjuvant imatinib is a medication used to help prevent the recurrence of gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST) after surgery. It works by targeting KIT mutations in the tumour cells, which can stop the cancer from growing and spreading. For patients with a higher risk of recurrence, imatinib is typically recommended at a dosage of 400 mg per day for a period of three years.
Common side effects of imatinib include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhoea
- Muscle cramps
- Fatigue
- Skin rash
- Fluid retention
- Abdominal pain
- Headache
Less common but more serious side effects can include:
- Hepatotoxicity (liver damage)
- Cardiotoxicity (heart issues)
- Severe fluid retention, leading to oedema
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- Low blood cell counts
Follow-Up Care
Post-treatment follow-up care is important for monitoring recurrence and managing long-term treatment effects. This includes:
- Regular imaging studies to detect any signs of recurrence.
- The frequency of imaging is based on the risk of recurrence.
- Patients receiving adjuvant therapy with imatinib should have CT scans 3 months after surgery, then every 6 months for 2 years, followed by annual scans up to 5 years (as per intermediate risk patients).