Using a handheld electric fan
- Cooling one’s face with a fan helps relieve breathing difficulties
- Method: Fix the fan at about six inches away from the face and let the cool breeze blow to the middle of the face. The patient should feel the symptoms relieving in a few minutes
- For first-time users, check if the patient shows any signs of discomfort, such as dizziness and cold. In case of discomfort, adjust the distance or wind speed of the fan.
- Consult the therapist in case of any enquiries
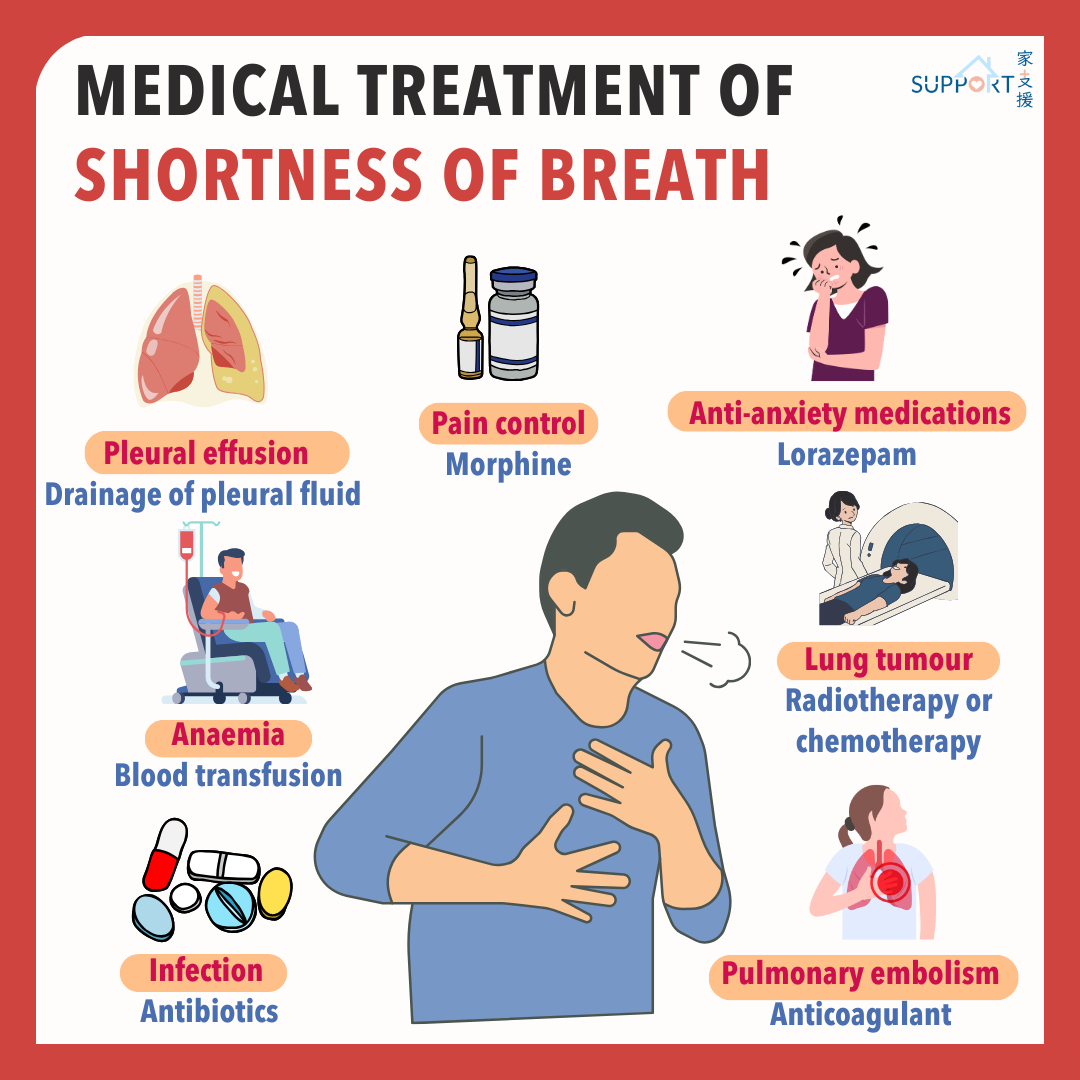
Postures to relieve difficulty breathing
- Relax the muscles and lower the diaphragm to alleviate difficulty breathing.
Sitting

- Lean forward, rest forearms on thighs or on a table with pillows. Rest feet on the floor with legs apart.
- This sitting posture allows the muscles to be in a better position to help breathing.
Standing
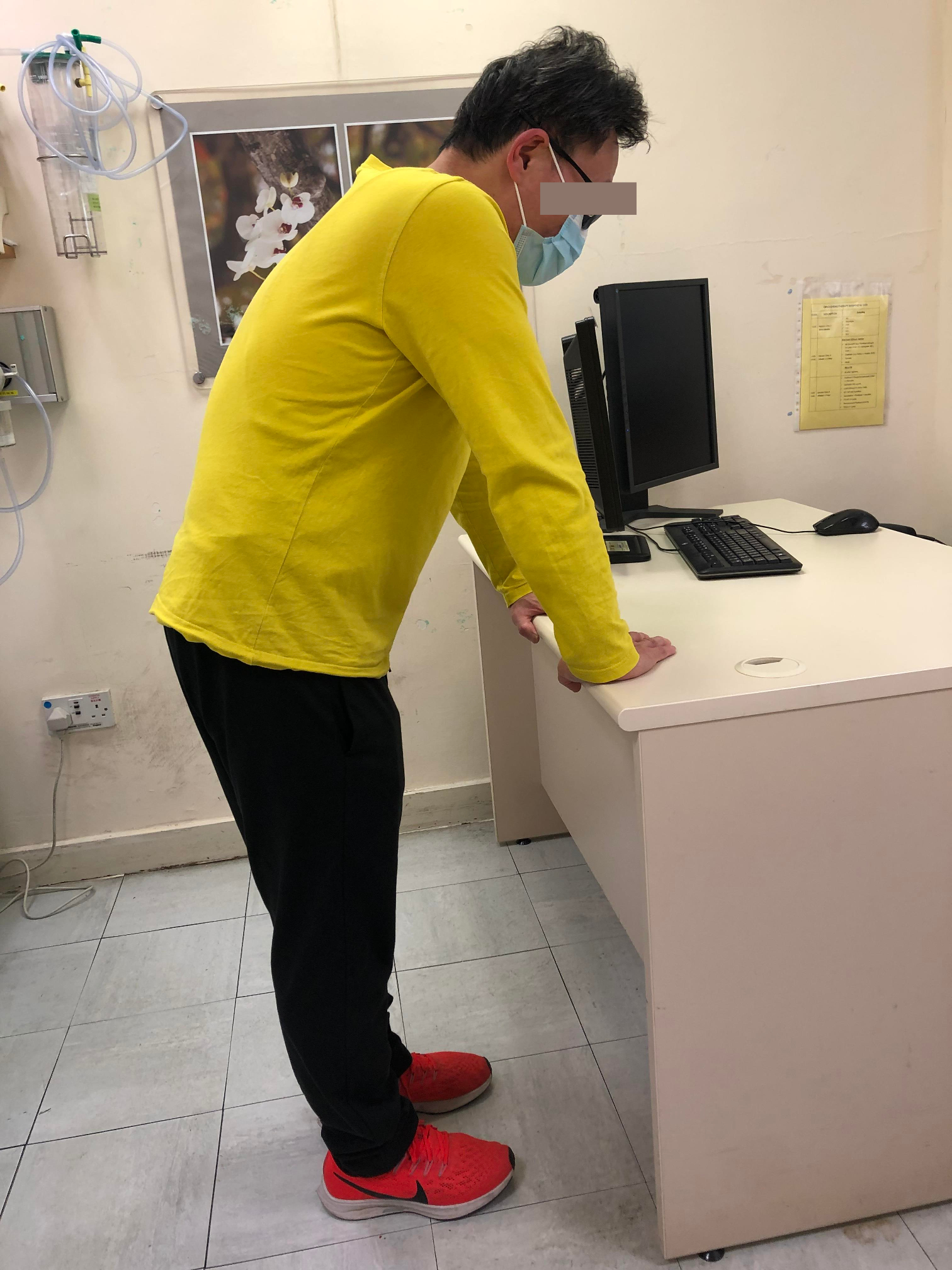
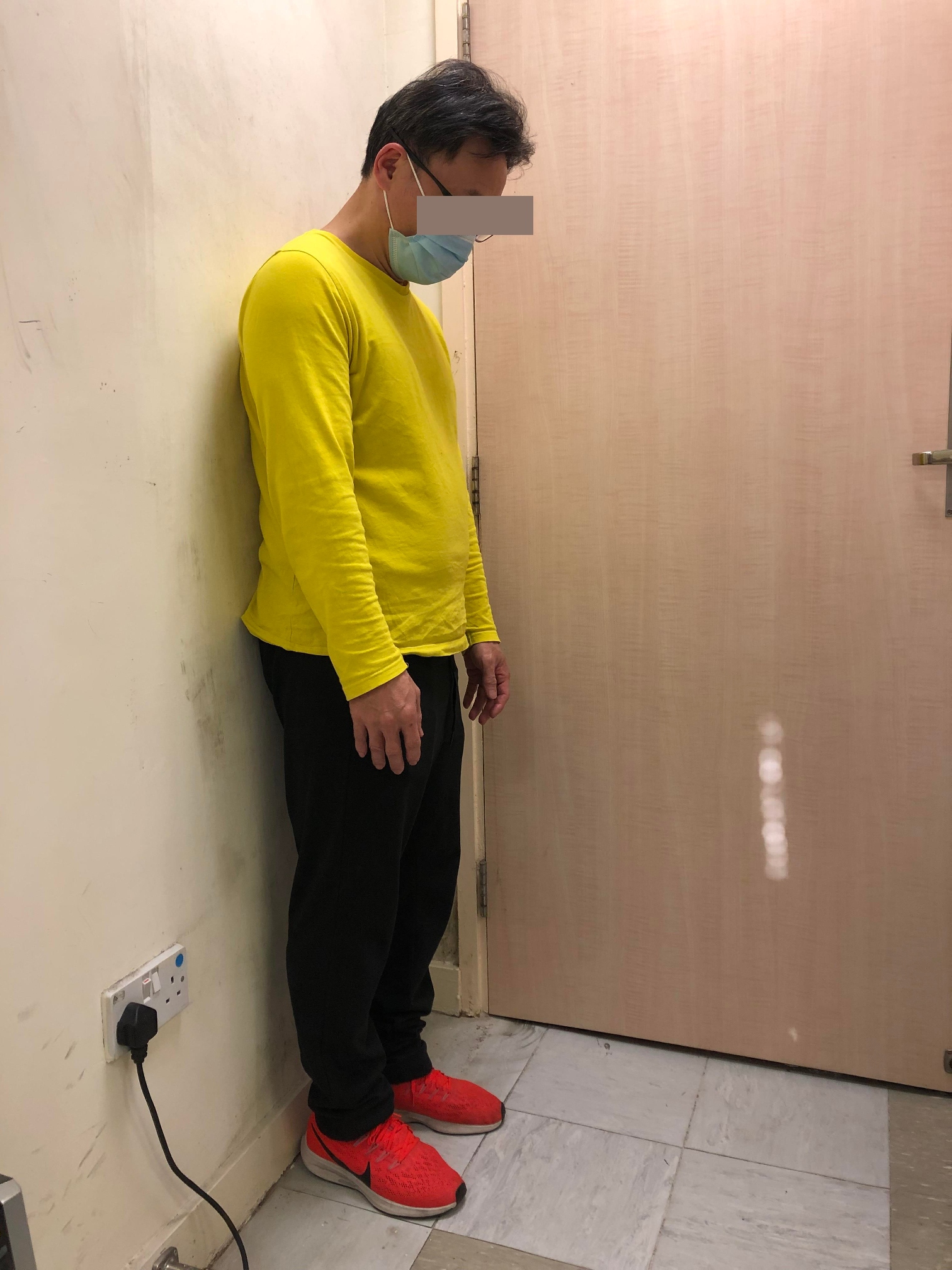


- If one cannot find anywhere to sit down, lean against some fixed or stable objects, such as wall, fence or a stable table.
Breathing techniques
- Mastering breathing techniques can help patients deal with the breathlessness. The following breathing techniques can be combined with handheld electric fan or the postures for relieving breathing difficulties.
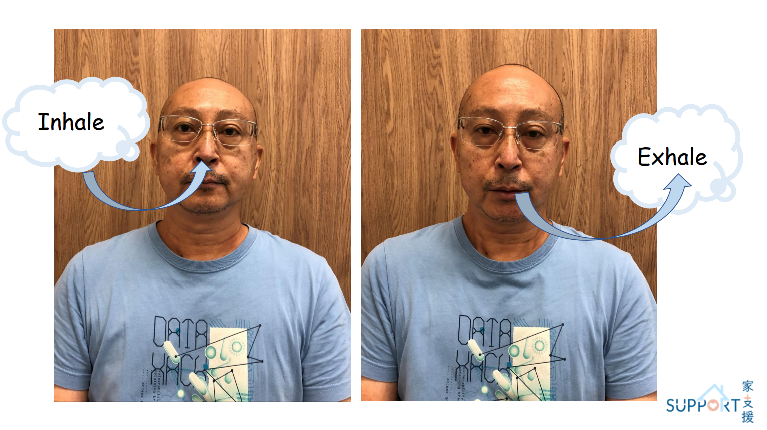
Pursed lip breathing
- When one breathes, one should first inhale through the nose in two seconds.
- Then purse out the lips to exhale as if one is blowing out a candle lightly. Last for four to six seconds. Do not exhale forcefully.
- The internal airway pressure created by exhaling through the pursed lips keeps the trachea open, making it easier to exhale air out of the lungs and leaving more lung space for the next inhalation.
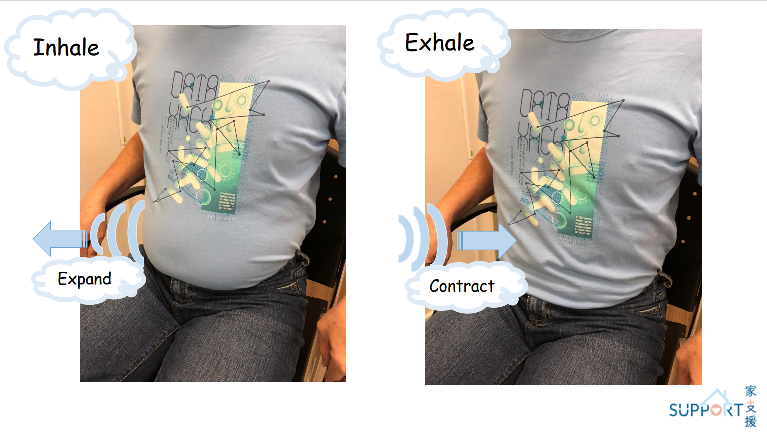
Abdominal breathing (diaphragmatic breathing) method
- Compared with breathing driven by upper chest, neck and shoulder muscles, this is a more effective breathing technique and less physically demanding:
- Gently place hands on the upper belly to relax abdominal muscles
- When inhaling slowly through the nose, try to inhale into the bottom of the lungs, while letting the hands rise gently with the bulge of the abdomen.
- When exhaling slowly with pursed lips, feel the abdomen drop.
- Rest and wait for the next breath
- At first, one may not be able to do the abdominal breathing naturally. One is recommended to practise more when you do not have difficulty breathing.
Do breathing relaxation exercises every day
Relaxation can help slow down breathing and improve breathing efficiency. If family members accompany the patient, they should gently stroke the patient’s back to reassure them and relieve anxiety.
Simple breathing exercise
- Stay relaxed, sit down, rest one’s back on a chair and one’s feet on the floor. One may also lay down and put your hands on your lower belly.
- Close one’s eyes and feel if one in still in a tense state.
- Slowly inhale through the nose and count to one.
- Slowly exhale through the mouth and count two and three. Imagine being in a peaceful and delightful place, such as a beach or field.
- Keep calm and relax the body and limbs. Repeat the inhalation and exhalation for three to five times, or until one is relaxed.
- When the relaxation exercise is about to end, count to three.
- Gently move one’s lower body
- Gently move one’s upper body
- Slowly inhale, open one’s eyes, exhale and tell oneself: “I feel comfortable physically and mentally.”
Plan your daily activities beforehand
- Excessive or overly intense activities may worsen breathing difficulties. Therefore, patients should rearrange their daily routine according to their ability.
- It is recommended that the patients plan their daily activities beforehand and set priorities. It may be necessary to organise the number of activities and arrange them at different times to save energy. Allow enough time to complete the tasks and arrange resting period when necessary.

- For more exertional activities such as taking a shower, one should control the breathing activities before they start, such as by placing a chair with a suitable height in the bathroom so that they may sit during the shower.

One may also arrange these activities after taking medication for control of breathlessness.
- For patients with mobility difficulties, consider using urinal, bed pan, bedside commode or mobile commode to assist toileting and showering. Carers should assess their own abilities, sponge bath or bed bath instead of bathing in bathroom when necessary, and seek help.


Recommendations for going outdoors and shopping
- One should try to match their breathing and walking pace. For example, take one step while inhaling and two steps while exhaling. Breathing steadily and avoid holding one’s breath. Walk at a comfortable pace and avoid walking too fast at a stretch.
- Use walking aids when appropriate and consider bringing a trolley when shopping

Stay active
- An appropriate amount of exercise can improve breathing and prevent muscle atrophy. Even if the patients have serious lung problems, they can still do a small amount of exercise. Consult the therapist in case of any questions.
Keep the indoor environment cool and fresh
- Use air conditioners, fans, dehumidifiers or air filters to keep the air fresh, dry and circulated.
Drink hot water if there is sticky sputum and saliva