Here are the main reasons why this happens:
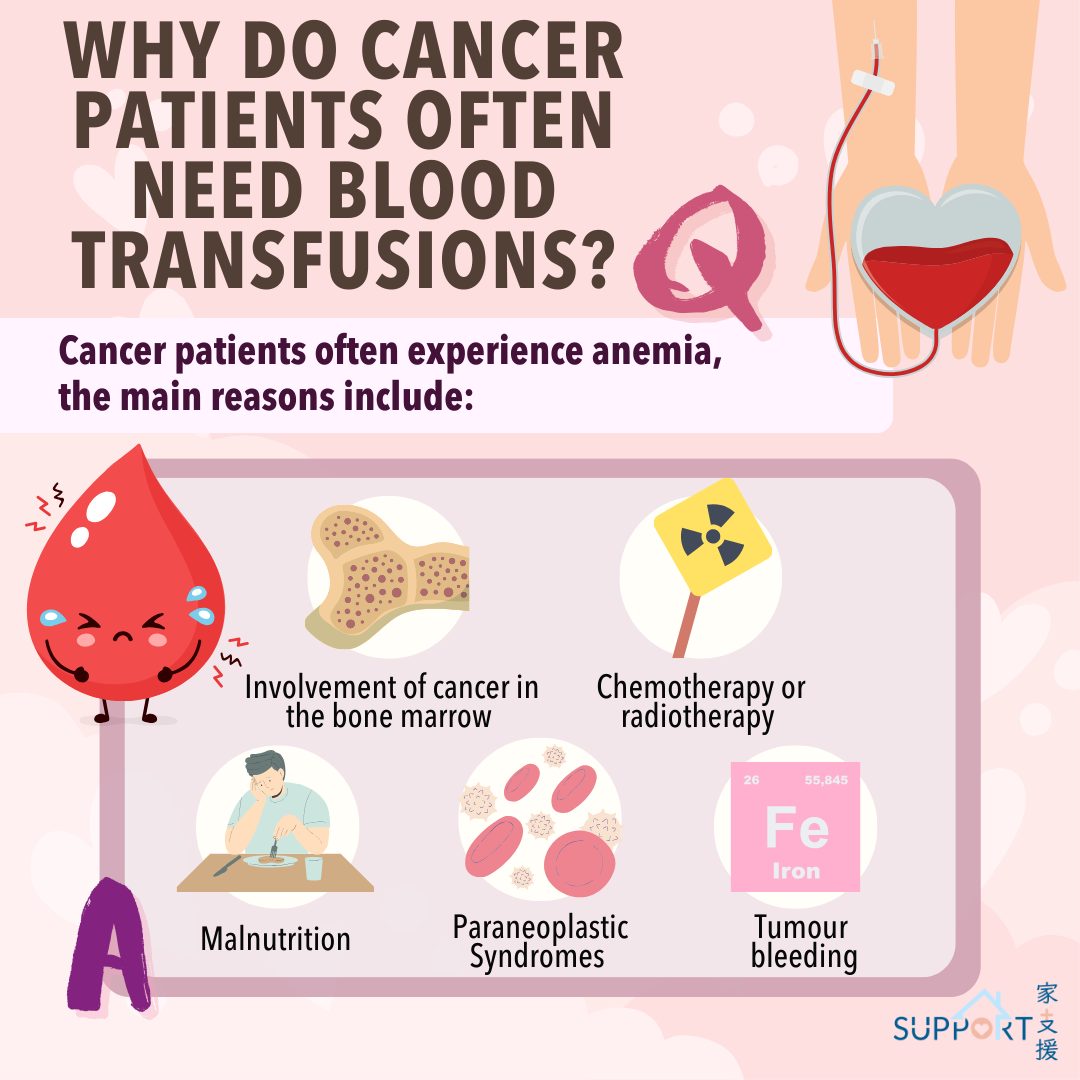
1. Involvement of cancer in the bone marrow 🦴: Cancer cells can invade the bone marrow, where red blood cells are made. This invasion affects the production of these cells, leading to anemia.
2. Chemotherapy or radiotherapy 💉: Treatments like chemotherapy and radiotherapy not only kill cancer cells but can also harm normal cell, especially the fast-growing bone marrow cells. This reduces the number of red blood cells (hemoglobin), causing anemia. Studies show that about 50% of cancer patients may develop anemia during chemotherapy.
3. Malnutrition 🤢: Poor appetite or digestive issues can lead to malnutrition. If the body lacks nutrients like folic acid, iron, or vitamin B12, it cannot produce enough red blood cells causing anemia.
4. Paraneoplastic Syndromes 🦀: Cancer releases substances that inhibit the production of red blood cells, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukins. These substances can speed up the breakdown of red blood cells, which is called hemolysis.
5. Tumor Bleeding 🌊: Certain cancers, such as stomach, colon, or cervical cancer, can bleed easily. If a tumor develops bleeding complications, it may lead to iron-deficiency anemia.


