Symptoms of hypercalcemia can be very non-specific. You may just feel a bit unwell or tired. More, the severity of your symptoms may not match with the level of calcium in your blood.
Some of the symptoms of hypercalcemia include:
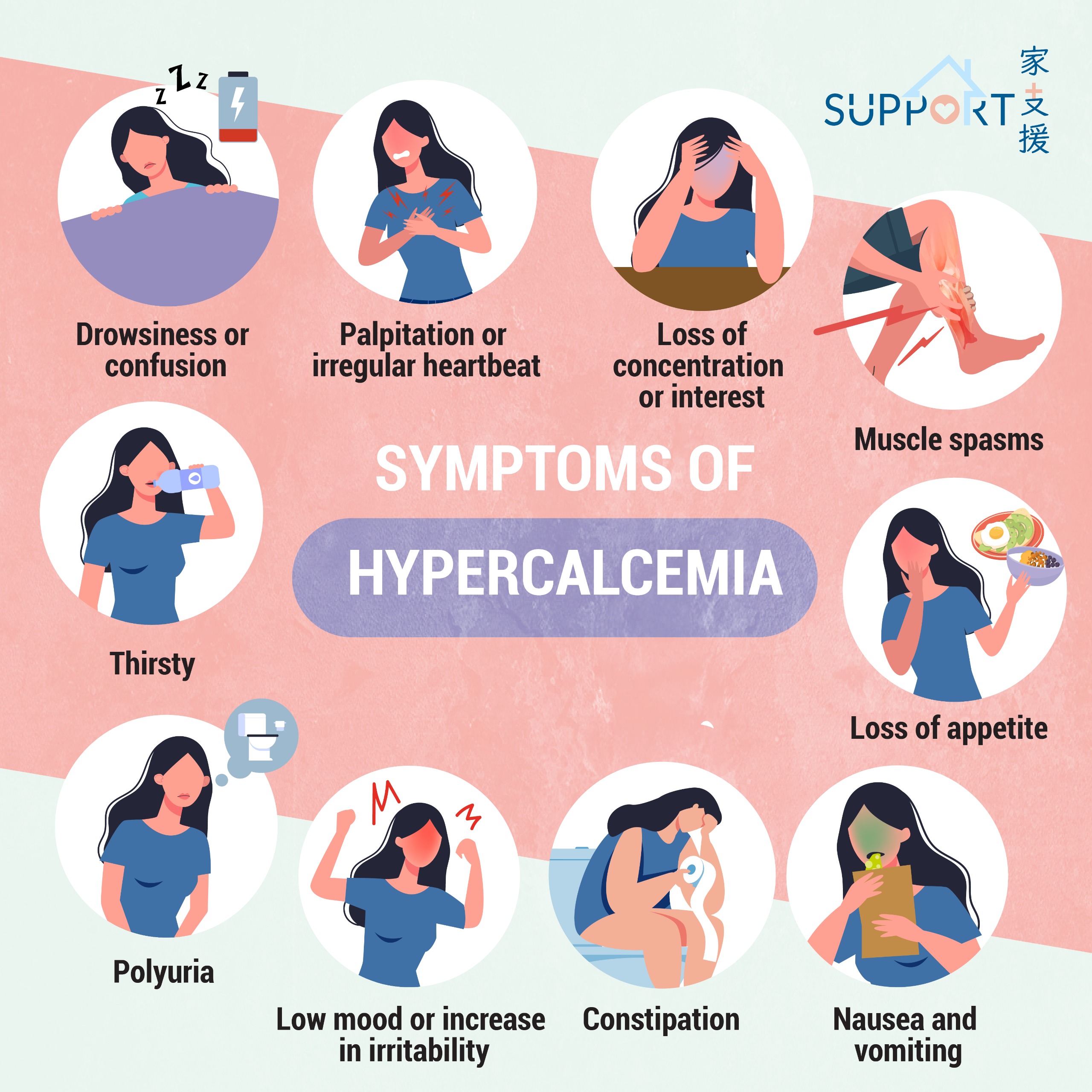
- feeling more tired than usual
- loss of appetite
- loss of concentration or interest
- constipation
- low mood or increase in irritability
- feeling thirsty
- passing urine more than usual
- dry mouth
- nausea and vomiting
- drowsiness or confusion
- muscle spasms
- palpitation or irregular heartbeat
If you have severely high calcium level, you might also have seizures or difficulty in muscle movement.


