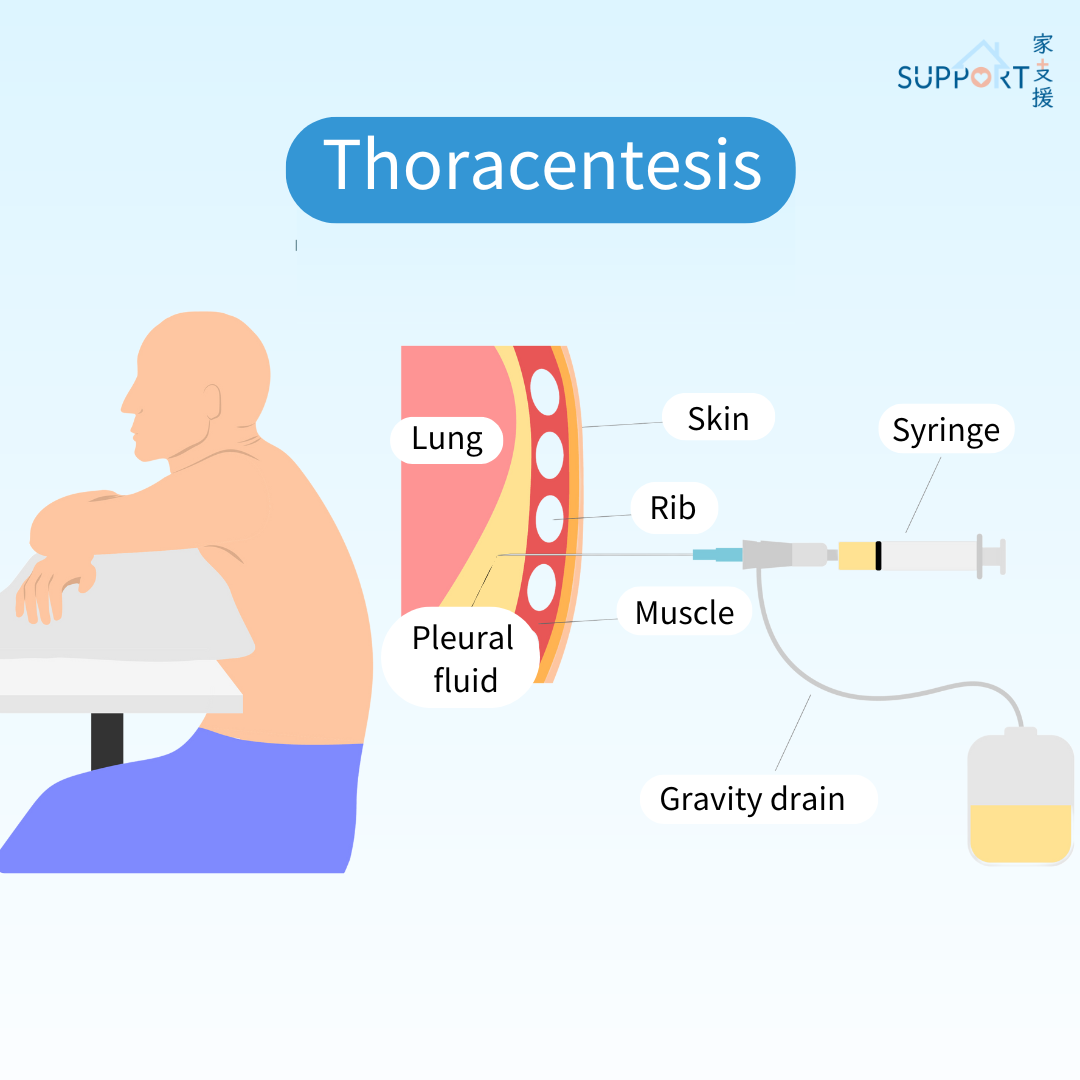
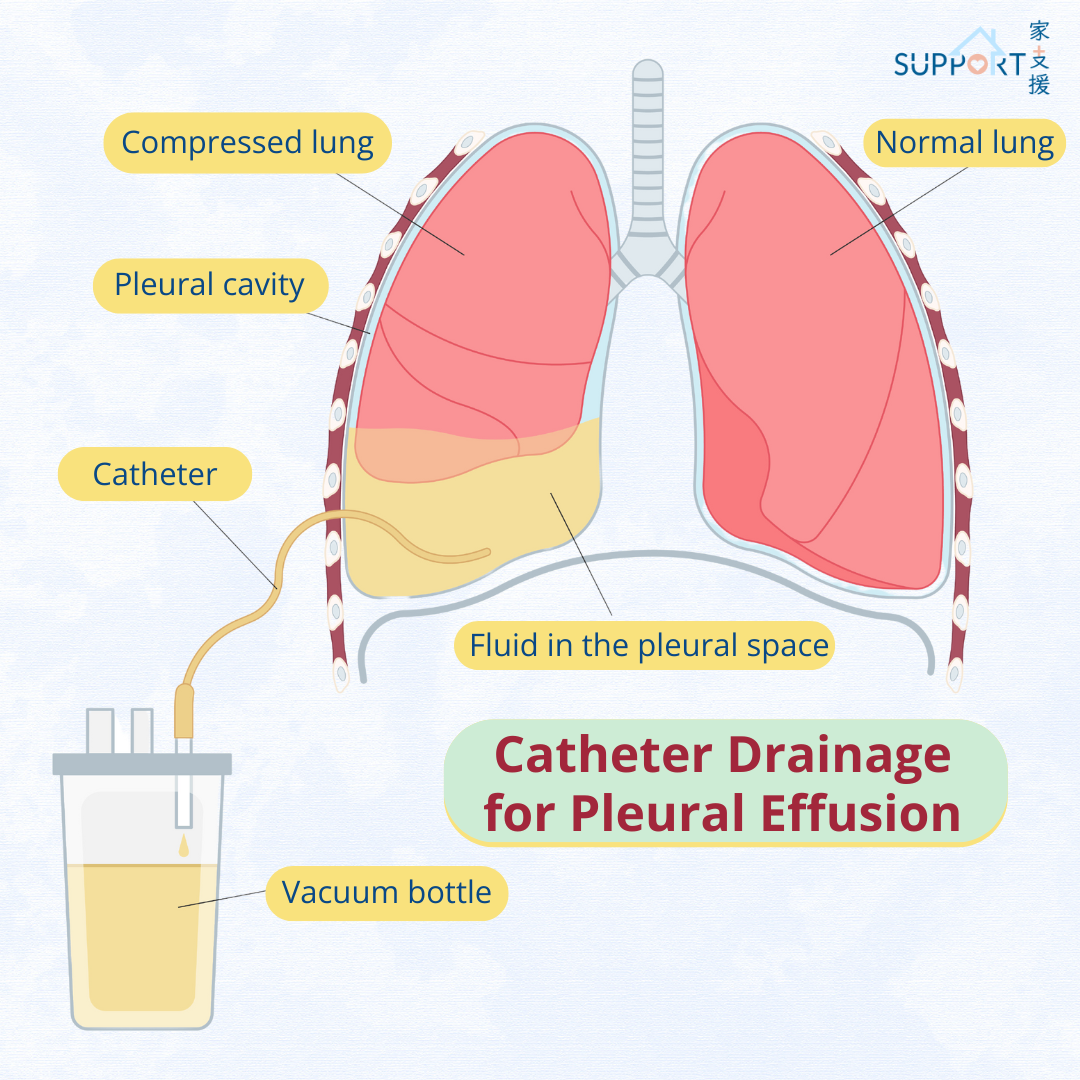
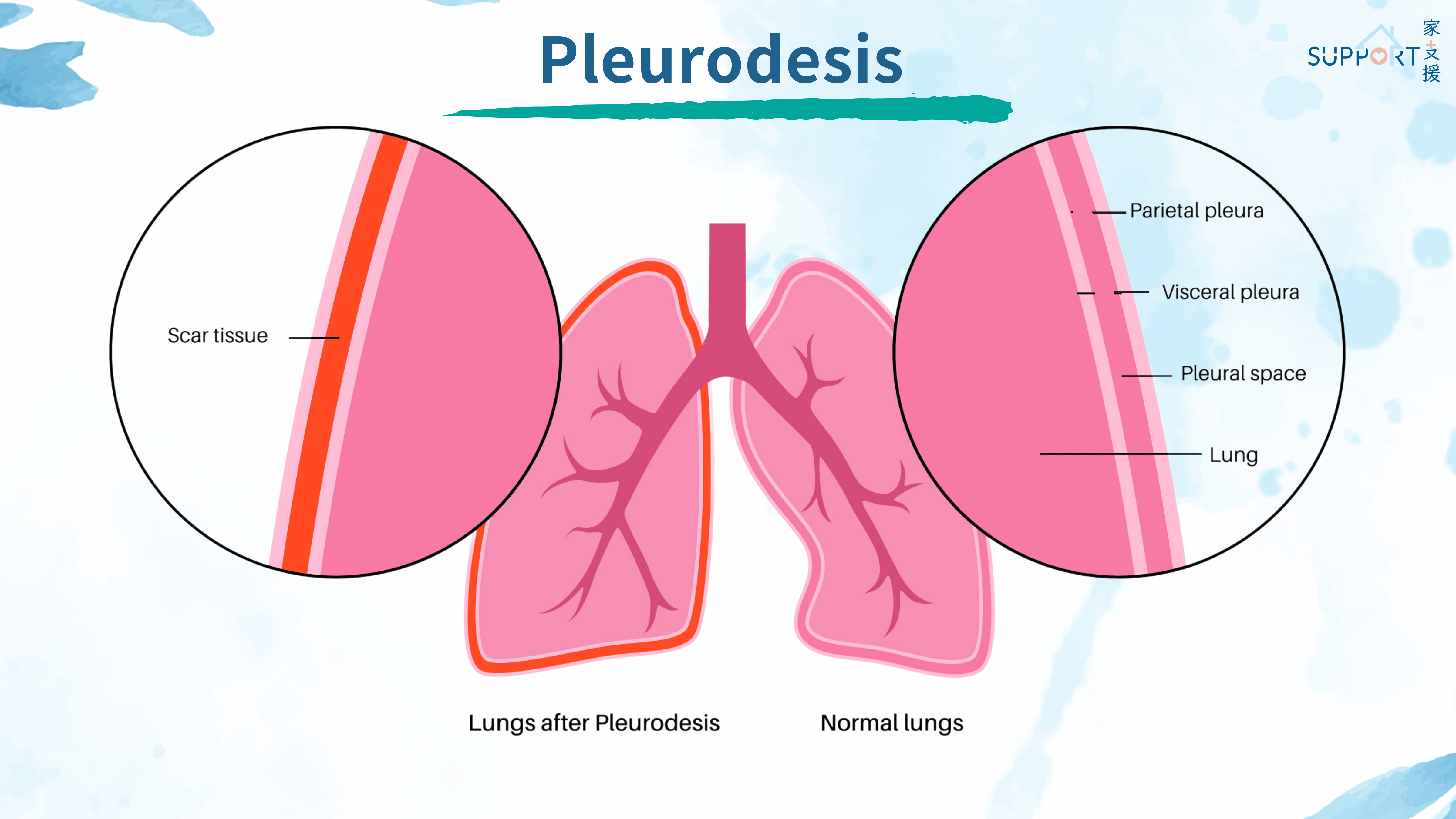
How is it different from pleural effusion?
Malignant pleural effusion is the buildup of fluid that collects between the lung and the chest wall caused by the spreading of cancer cells.
There are two layers of tissues that cover and protect the lungs. They are called pleura (or pleural membranes). Between the 2 pleura is a space called the pleural space, which contains a very small amount of fluid (approximately 1 teaspoon) that helps the lungs move easily during breathing. Pleural effusion occurs when there is excessive fluid buildup in the pleural space. This makes the expansion of lungs more difficult, leading to difficulty in breathing.
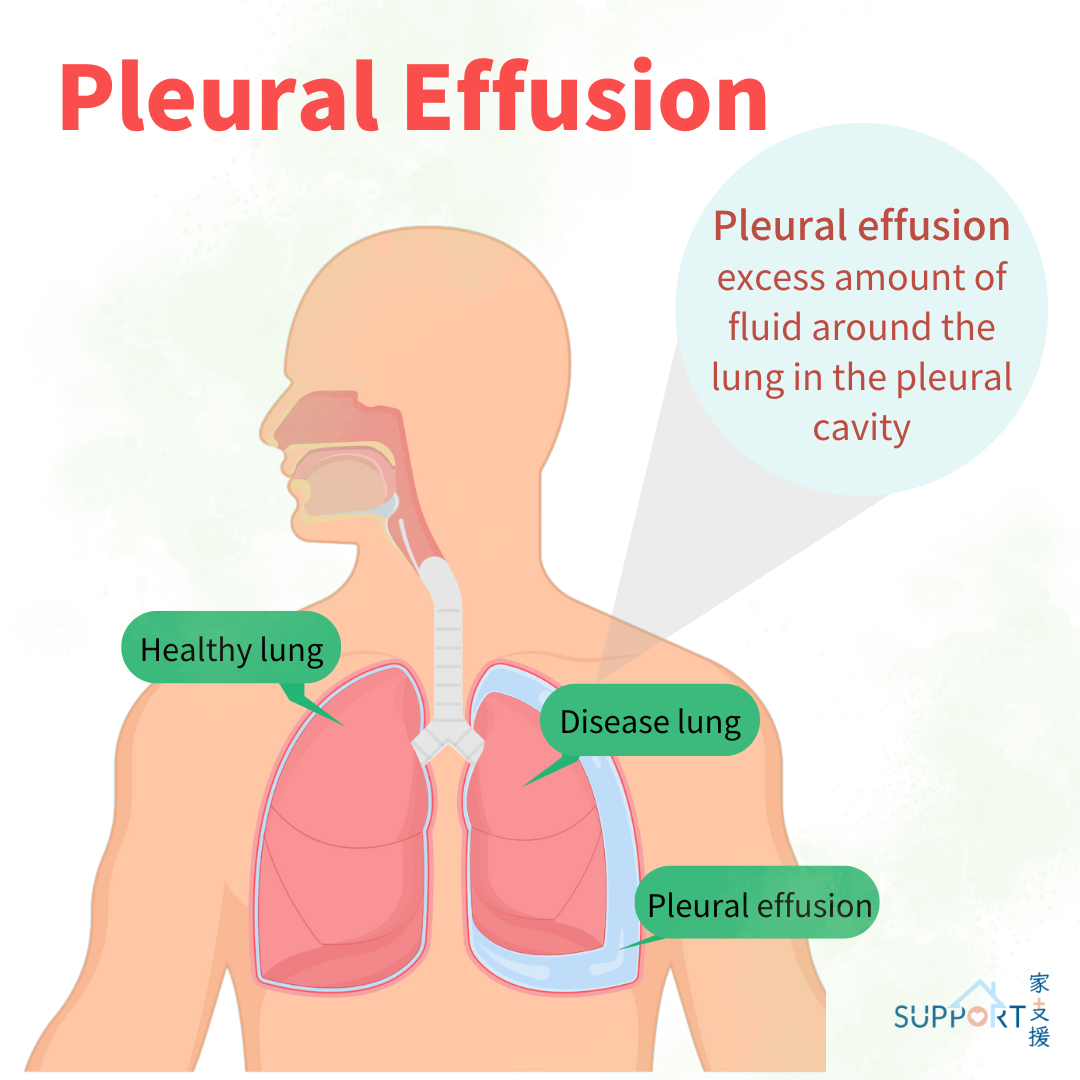
Malignant pleural effusion is a specific type of pleural effusion caused by cancer. The cancer cells increase the production of pleural fluid and decrease the absorption of the fluid, causing an accumulation of fluid.