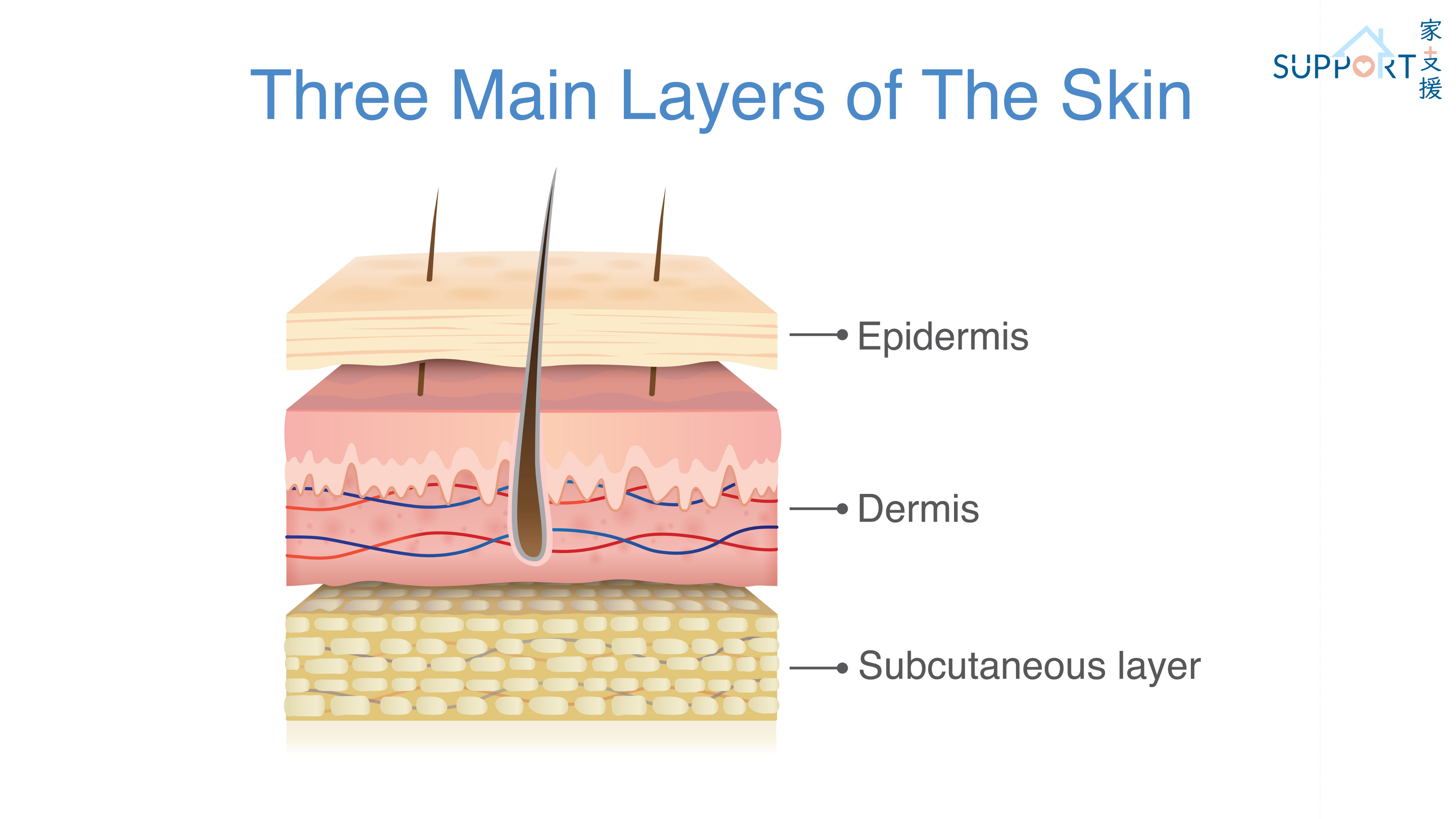
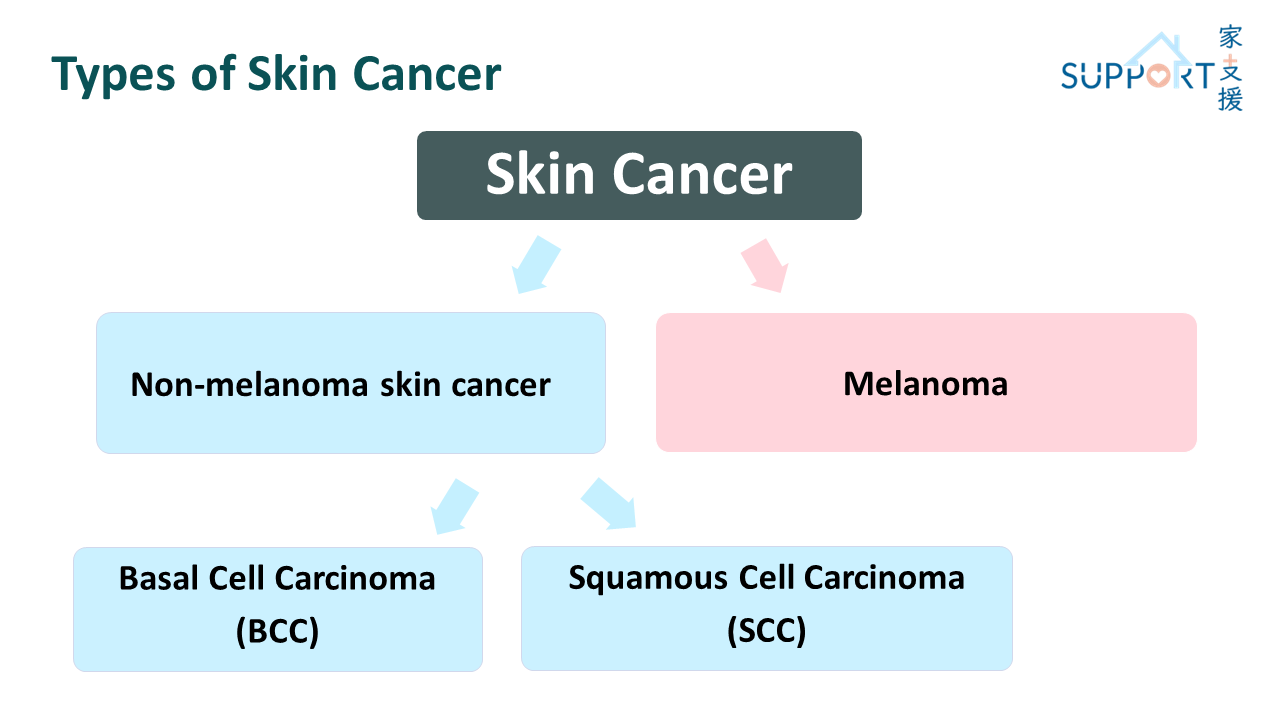
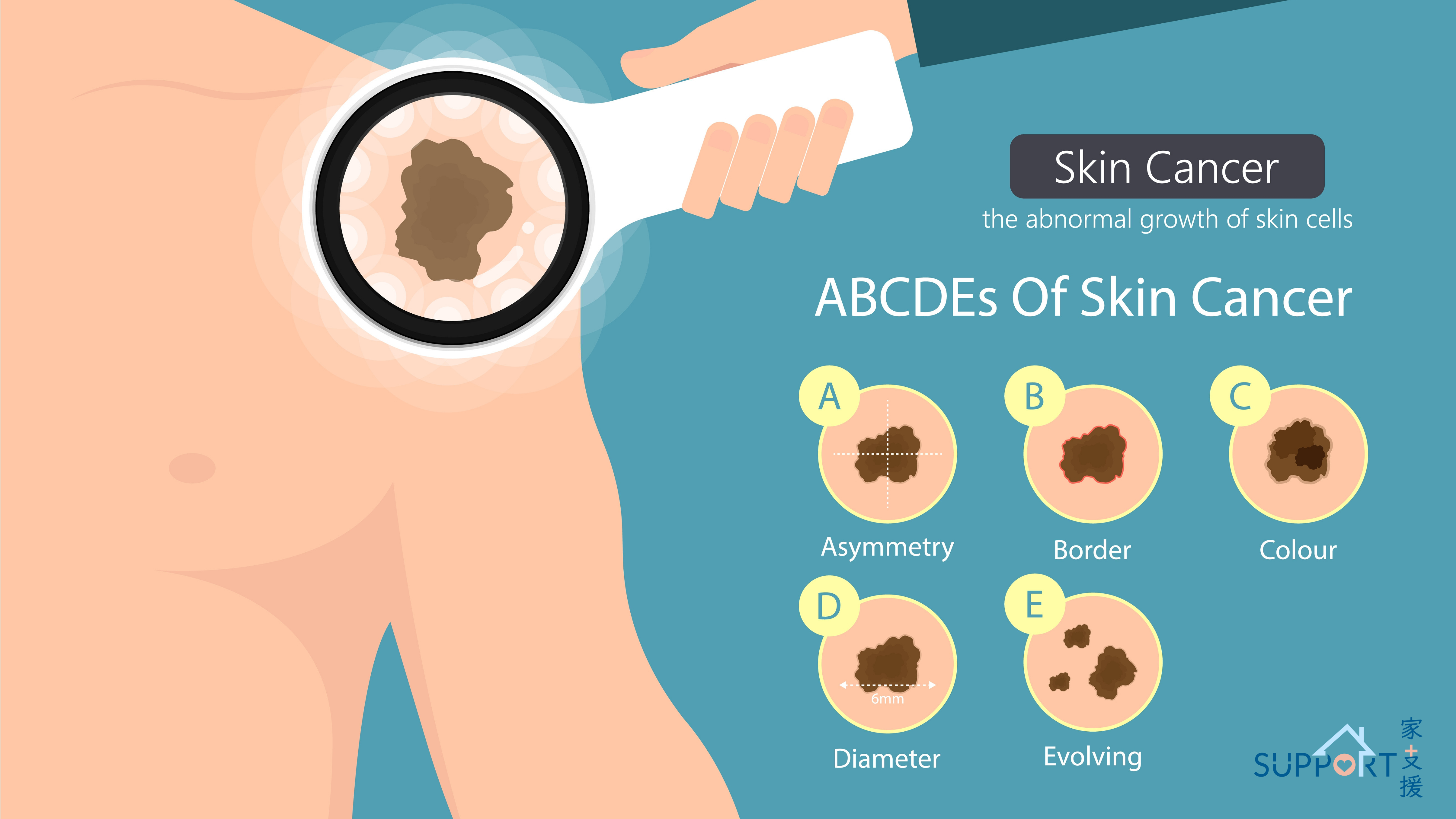
American Society: Skin Cancer
Cancer Council: Skin Cancer
Macmillan Cancer Support: Skin cancer
NCCN Guidelines for Patients. Basal Cell Skin Cancer, 2022.
NCCN Guidelines for Patients. Melanoma, 2024.
NCCN Guidelines for Patients. Squamous Cell Skin Cancer, 2023.
NCCN Guidelines. Basal Cell Skin Cancer. Version 1.2025.
NCCN Guidelines. Melanoma: Cutaneous. Version 1.2025.
NCCN Guidelines. Melanoma: Uveal. Version 1.2025.
NCCN Guidelines. Squamous Cell Skin Cancer. Version 1.2025.
Smart Patient (by Hospital Authority): Skin cancer
Special thanks to Ms. Locani Hing-Wai Wong (Class M25), Mr. Alex Yung-Pok Lee (Class M25), medical student of Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, the University of Hong Kong, and Dr. Wendy Wing-Lok Chan, Department of Clinical Oncology, the University of Hong Kong for authoring and editing this article.
Last updated on 19th Jan, 2025.